Contents [hide]
1. Security Education
There are 2 important components of security training programs.
Security training: this provides users with the knowledge they need to protect the organisations security
Security Awareness: Keeps the lessons learned at the front of the users mind. EG: posters, email reminders etc…
Security Training Methods
- instruction in onsite classes
- as part of new staff induction or orientation
- education through online providers
- participation in vendor provided classroom training
Example of training programs
This site offers training modules that customisable. https://www.sans.org/security-awareness-training/products/end-user
This site allows you to conduct fake phishing attacks: www.phishme.com
Training Content & Frequency
Different roles need different levels of training. i.e.: IT support staff need different training than a receptionist. You need to cater for their needs accordingly.
Training frequency:
- initial training for new employees
- update training for employees in roles
- refresher training on a annual basis
2. Information Classification
Data Classification Policies
These policies assign information into classifications that determine storage, handling and access requirements.
Information classification is based upon:
- sensitivity of information
- criticality of information
Classification Levels
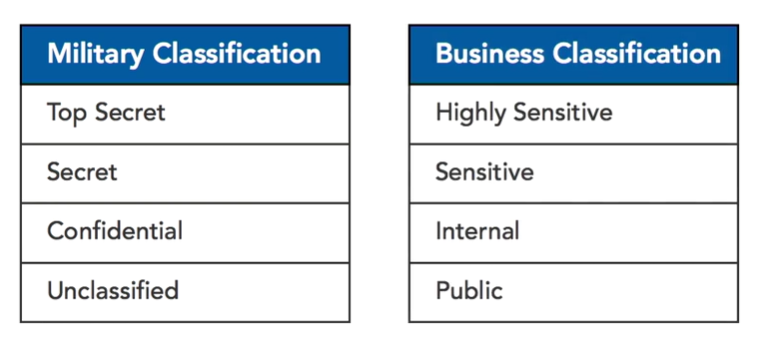
Classification guides other security questions, EG: should this data be encrypted?
Information in classifications should be labelled correctly.
Secure Disposal Procedure
When devices are being sold or recycled the drives must be wiped correctly using something like DBAN
3. Compliance Training
Compliance programs ensure that an organisations information security controls are consistent with the laws, regulations and standards that govern the organisations activities. Compliance requirements differ a lot between organisations. EG: a University will have different requirements to a retail shop. Compliance obligations should be covered in security training. EG: if a law requires that employees never write down credit card numbers, employees should be made aware of this in training.
3 types of Compliance Obligations
- Laws: these come with civil or criminal penalties for failure to comply. EG: in financial firms there are laws that state they must have an Information Security Officer and a formal Information Security program in place to protect customer information.
- Regulations: these are mandatory requirements that an organisation must follow but are not embodied by law.
- Standards: these are detailed technical specifications for security and other controls. Organisations may be required to comply with standards by a contract or regulation.
4. User Habits
User habits education programs should address:
- password security practices
- data handling procedures (how data is handled and destroyed)
- Physical security training (no tailgating into buildings)
- BYOD policies should be covered
- Appropriate use of social media
5. User Based Threats
This was covered in other chapters: https://www.spktechfit.com/?p=159#1412_Social_Engineering_Attacks
6. Measuring Security Education
It is important that organisations take steps to measure the effectiveness of their security education efforts. Some methods include:
- Simulated phishing. this directly measures user awareness
- Security awareness surveys. EG: “How well does the organisation prepare you to deal with security threats?”, “Do you know where to report a security incident?”
